Diamond 軟體的開發公司 Crystal Impact Gbr,成立於 1997年,其成立的目的是要開發優質的化學軟體;即使不是專家的使用者都能上手。Diamond 主要具有以下功能:晶體結構的求解、視覺化、材料資料庫和材料設計。全球有五十個國家以上的化學家和材料科學家(包含學術界和產業界)都在使用Diamond 來決定、視覺化和了解他們所在研究的化合物。
Diamond 是 Windows平台上用來觀察和繪製晶體結構的軟體,能處理的資料容量高、功能多(從開始的分子產生到複雜的無機結構)。Diamond 是分子、固體化學、表面和材料學家不可或缺的工具。
特色
Input and Output:
- Proprietary binary Diamond 3/4 Document format (extension .diamdoc) :
- Supports both crystal and molecular structures (i.e. with and without translational symmetry).
- Storage of multiple structure data sets in a document, each with:
- atomic parameters,
- cell parameters and space-group (optional),
- anisotropic displacement parameters,
- connection parameters (bonds, H-bonds, non-bonding contacts)
- chemical and bibliographic data (author, reference, database origin, etc.).
- Supports multiple structure pictures for a structure data set. Saves your own built-up and designed frameworks of crystal structures.
- Compatible with Diamond 2 format (DSF).
- Number of atoms, bonds, polyhedra etc. limited only by RAM.
- Manual input or update of chemical, crystallographic, and bibliographic data.
- Automatic import from data formats:
- CRYSTIN download format created by ICSD or CRYSTMET
- Cambridge Structural Database FDAT format.
- Brookhaven Protein Data Bank format.
- SHELX-93 format.
- Crystallographic Information File (CIF).
- XYZ format (free format with cartesian coordinates),
- SYBYL MOL and MOL2 format,
- Cerius2 (CSSR) format,
- MDL MOL format.
- Export of structure data to:
- CIF,
- SCHAKAL,
- XYZ format.
- POV-Ray assistant to create photo-realistic scenes with shadows, reflections, textures, background graphics, and more.
- Export of structure picture's 3D world to:
- Wavefront OBJ (plus MTL materials definition file),
- STL (text format),
- VRML 1 (WRL files).
- Export of structure picture's 2D graphics (for post-processing e.g. in a word processor or graphics application):
- as Windows metafile (WMF, vector-oriented),
- as bitmap (BMP; width, height and resolution user-defined),
- as GIF, JPG, or PNG file, e.g. to link with an HTML document.
- Cut, Copy, or Paste of data sets between documents (together with associated structure pictures). Enables creation of small "databases".
- Search for chemical, crystallographic, or bibliographic data:
- in files of selected types in selected directories,
- in "Crystallography Open Database" (COD), including (amongst others) AMCSD ("American Mineralogist Crystal Structure Database") as well as CIF files from the IUCr journals, cf. "www.crystallography.net".
- Small database of most frequent (inorganic) structure types, e.g. to insert structure data or ready-defined structure pictures from.
- Configurable list of structure data sets in a document:
- as table ("structure list")
- or in collapsed form as "structure info bar".
- Color coding to differentiate structure data sets in a document with multiple structures.
- Thumbnail overview of structure pictures of a selected data set or of the whole document.
- Recent picture list with thumbnails of last edited pictures/documents.
- Data sheet for textual representation of structure data:
- in compact or comprehensive form
- or with customized selection and order of items.
- "Atom list": Hierarchical list of atoms in structure picture, groupes by atom sites and/or groups or by molecules.
- Printing of selected datasets, data sheet, tables, or structure pictures. Textual copy of datasets via Windows clipboard for post-processing.
- Export of data sheet and tables as HTML.
Construction:
- Optional assistant that helps to create a structure picture from scratch or to modify a picture.
- "Auto Picture Creator" - available in a docking window side-by-side with the structure picture - to interactively change picture building as well as picture design and viewing direction.
- "Building schemes" (in Diamond 3 called "Auto-Builder") that create pictures automatically or according to a user-defined strategy. Useful when visualizing a lot of similar structures.
- Conversion between "crystal" and "molecular" structures, i.e. adding or removal of cell and symmetry information.
- Filling of unit cell, multiple cells, any cell range, or boxes or spheres around selected central atoms.
- Filling of user-defined rectangular areas within the screen.
- Filling of slabs along a plane (hkl or least-squares) or between a plane and the walls of the coordinate system.
- Selection of atoms to construct sublattices ("Filter").
- Support for disorder parts when searching for neighbouring atoms and bonds as well as in "Filter" function.
- Creation (and discussion) of atomic environments, optionally from Dirichlet domains of the atom sites.
- Discussion of connectivity assisted by histograms showing the distribution of distances between selected atom types and from the bond parameters, together with automatic calculation and checking of distance ranges.
- Creation of bonds automatically, basing on connecitivity, or manually by inserting bonds between two atoms each.
- Adding all atoms (and optionally bonds, H-bonds, contacts) of atomic parameter lists as well as from connection parameter lists.
- Generation of atoms from parameter list serving as initial atoms for building up complex frameworks.
- Completion of coordination spheres around selected atoms.
- "Pump up": Generation of multiple spheres around selected atoms and its reversal ("shrink").
- Automatic generation of molecules or completion of fragments which have e.g. been clipped at cell edges.
- Definition of molecular units (from atomic parameter list).
- Generation of molecules from molecular units at symmetry-equivalent positions.
- Search for molecules in the neighbourhood of selected atoms or molecules.
- Creation of molecular packings (parallelepiped, sphere, slab, or layer).
- "Grow" and "cut: Expansion and reduction of polymers or molecular fragments.
- Creation of "broken-off" bonds to signal infinitesimal chains, layers, or 3D-frameworks. Conversion between "broken-off" and normal bonds.
- Definition of H-bond and non-bonding contact connectivity. Creation of H-bonds and contacts.
- Expansion to neighbouring atoms or molecules via H-bonds and/or contacts to build up molecule clusters and reversal ("reduce").
- Discussion of contact spheres and expansion or reduction of molecule clusters with the mouse wheel.
- Cut, copy and paste of structural parts between structure pictures:
- A fragment of a structure picture (or the whole picture) can be copied.
- The copied fragment can be pasted into a blank or another picture of the same data set.
- User-controlled dismantling of built-up frameworks.
- Multiple-step Undo and Redo function (with picture thumbnails) to enable safe experimentation with even high-complicated and unknown structural frameworks.
Visualization:
- "Design schemes" (a kind of style sheets) containing picture design and viewing settings for quick-and-easy application to other structure pictures.
- Layout modes:
- Regular/window,
- for printout, e.g. A4 page size with white background,
- for creation of a bitmap with given x and y dimension and a resolution in dpi.
- Variable zoom factor (enhances "Page view" mode of Diamond 2).
- Models, assigned globally or individually to single or groups of atoms (allows mixing of different models in one and the same picture):
- Ball-and-stick (regular),
- ellipsoid,
- space-filling,
- sticks or wires (depending on bond radius).
- Definition of views along special axes or toward special planes.
- Central or parallel projection, depth cueing, and stereo display.
- Photorealistic rendered models with user-defined light source and material properties (OpenGL).
- Variation of colors, styles and radii of atom groups and bonds. Individual design of each single atom is possible.
- Variation of atom and bond radii with mouse wheel.
- ORTEP-like atom styles (ellipses, octants) in both flat and rendering mode.
- Optionally fragmentated and two-colored bonds.
- Optionally adjustment of atoms' and bonds' transparencies to site occupation factors.
- Optionally random distribution of mixed sites' components.
- Labelling of atoms and bonds. User-defined text, can be placed at arbitrary position of picture.
- Generation of coordination polyhedra:
- Around central atoms of selected groups or around individually selected atoms,
- built up from selected ligand atoms,
- optionally with transparent or hatched surfaces.
- Enhanced construction of coordination polyhedra:
- Defining corners and edges by selecting (clicking on) atoms and bonds, rsp.
- Removing of edges to increase triangles to higher polygons.
- Copy and Paste of polyhedron buildings between atoms of same site each.
- Definition of (transparent) lattice planes and (best) planes or lines through selected atoms.
- Adding of vectors to atoms to indicate e.g. a magnetic moment.
- Alternative color differentation to visualize oxidation numbers, site occupation factors etc.
- Full screen view (with window frame, menu, toolbars hidden).
Animation:
- Movement of structure picture:
- Modes:
- Rotation along x-, y-, and/or z-axis,
- horizontal and/or vertical shift within drawing area,
- variation of enlargement factor (from Angstroems to centimeters),
- variation of camera distance (perspective impression).
- Controlled by:
- Mouse (the faster the mouse the faster the rotation etc.),
- keyboard (e.g. one degree rotation per keystroke),
- numerically (input through dialog).
- Optional "Spin" function, i.e. acceleration of movement.
- Continuous movement, which can be interrupted and continued.
- Modes:
- "Grab mode": Arcball rotation of an atom under the mouse cursor. Shifting with the right mouse button pressed. Changing the enlargement factor with the mouse wheel.
- Walk-through mode, enabling the camera/viewer to navigate through the structure picture.
- Recorder that helps to create video sequences, e.g. as AVI files.
- Creation of POV-Ray image sequences or videos from recorded pictures or from animations on a single structure picture.
Exploration:
- Neighbourhood preview of atom under mouse cursor with radius of preview sphere variable with mouse wheel .
- Calculation of powder pattern:
- Variation of diffraction parameters:
- Radiation type: X-ray (laboratory, synchroton), neutron, electron,
- wavelength,
- LP correction,
- 2theta range,
- optional profile functions.
- Diffraction diagram (styles, colors and line weights can be configured).
- Table of reflection parameters with zoom in/zoom out and tracking through 2theta range.
- Variation of diffraction parameters:
- Calculation of distances and angles (incl. standard uncertainties):
- in a configurable table, for selected atom types and a sizeable distances range,
- around the atom(s) currently selected in structure picture.
- Graphical representation of distances as histogram with color-coded distances.
- Measuring of distances, angles, and torsion angles interactively (incl. standard uncertainties).
- Measuring of extended geometric features (incl. standard uncertainties):
- Angle between two planes (by hkl or (best) plane through 3 or more atoms),
- angle between two lines,
- angle between a normal of a plane and a line,
- distances of atoms from a plane or a line,
- centroid of a set of atoms,
- planarity or linearity of a set of atoms (distances of constituent atoms from plane/line).
- New Properties pane, displays information about:
- Contents of the structure picture (how many created atoms, bonds, polyhedra, etc.),
- the current "formula sum", that means the number of created atoms associated to atom groups,
- Info about the object that is selected in the structure picture or in the (optional) table above the properties pane, e.g. info about an atom of the parameter list,
- Table of the currently selected objects,
- Distances around the selected atom(s),
- Distances between the selected atoms,
- The center of the selected atoms (centroid),
- The planarity or linearity of the selected atoms and the deviations of the atoms from that plane or line, rsp.,
- Table of atoms assigned to the selected atom of parameter list or selected atom group,
- Table of bonds assigned to the selected bond group (i.e. atom group pair),
- Ligand, edges, and faces informations of the selected polyhedra.
- Dirichlet domain of a selected atom site.
- Neighbouring atoms and vertices of a selected Voronoi polyhedron.
More new features:
Animated POV-Ray pictures or video sequences from POV-Ray pictures, support for disorder parts, improved mixed sites representation, export of 3D scene into OBJ and STL format. (User-defined symmetry and visualization of symmetry elements, bond valences, and calculation of powder pattern using Debye formula to come in minor updates 4.7 or higher.)
系統需求
System requirements
To install and run Diamond Version 4.0 or higher, you should have the following system requirements:
- Personal Computer with Microsoft Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8/8.1, Windows 10, or Windows 11 operating system. (Note: does not run with Windows RT and does not run with Windows 10 when in "S mode".)
- Microsoft Internet Explorer 8 or higher
- Intel or AMD (or compatible) processor with "x86" instruction set
- 1 GB of RAM
- 3.8 GB of free disk space (6 GB during installation procedure, for unpacking of Crystallography Open Database)
- Graphics resolution of 1024 x 768 pixels with 32,768 colors ("High Color") or higher (1280 x 800 pixels or more recommended)
- DVD-ROM drive (for installation from DVD)
- Microsoft-compatible mouse
Endeavour
Structure Solution from Powder Diffraction
Endeavour is a powerful software for crystal structure solution, both from powder as well as single crystal diffraction data. Based on more than ten years of experience, the software is capable of solving many small to medium sized structures more or less on its own. The innovative concept combined with the elaborate user interface makes the solution of crystal structures an almost routine process, especially for inorganic but also for many organic compounds.
Even unexperienced users can prepare and perform the structure solution calculation in a few steps: Simply follow the integrated "wizard" to enter the required data (unit cell parameters, chemical composition, diffraction data), and let Endeavour do the rest. The structure solution is performed using a special variant of the "direct-space" approach, namely a combined global optimization of the difference between calculated and observed diffraction data and of the potential energy of the system. Due to the additional usage of the potential energy, the method is much less sensitive to low-quality diffraction data than e.g. direct methods.
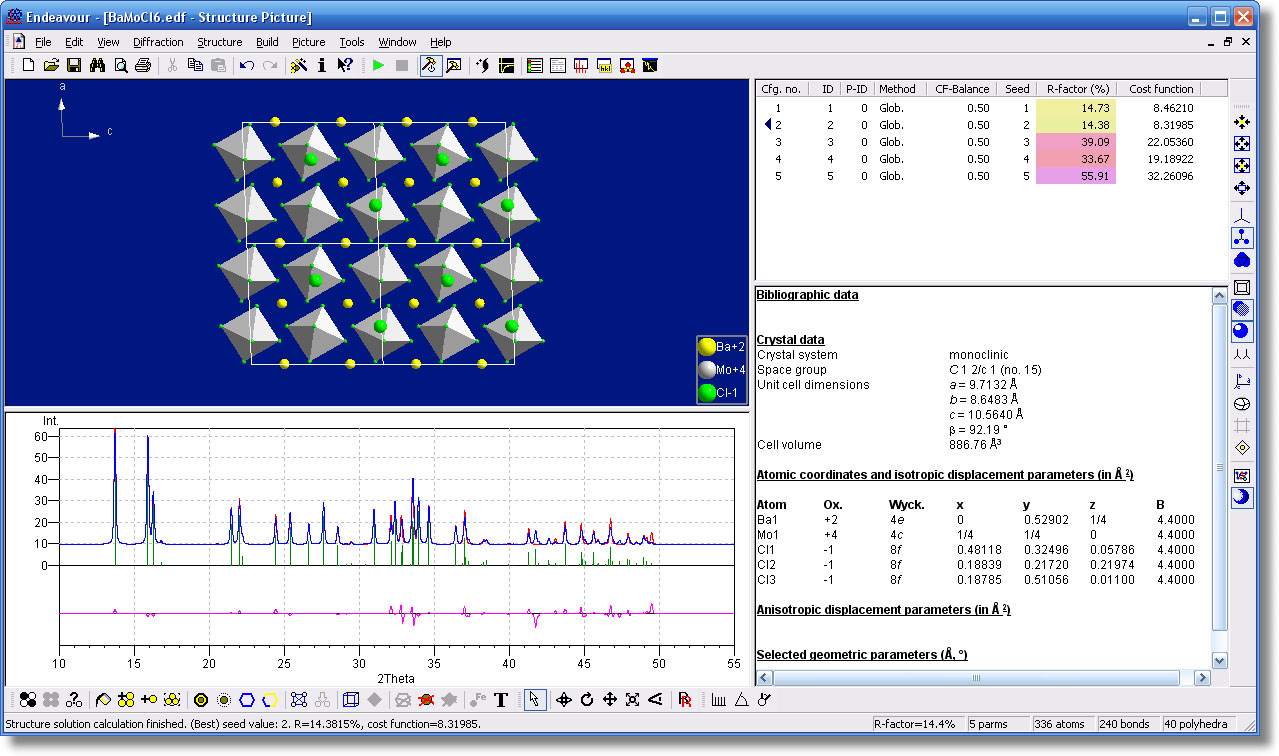
特色
Structure Solution:
- Structure solution from conventional X-ray laboratory diffractometer as well as synchrotron, neutron or electron diffraction data
- Input required:
- unit cell parameters
- diffraction data: either powder diffraction data (integrated intensities at Bragg angles (not profile/step-scan data), imported from Philips, Bruker-AXS, Stoe), or single crystal diffraction data (I(hkl), |F(hkl)| or F2(hkl)), e.g. imported from SHELX-file
- contents of the unit cell (composition or molecular structure plus number of the formula units)
- "Wizard" for the easy preparation of the input data
- Automatic adjustment of all structure solution calculation parameters
- Calculation of profile patterns from experimental and calculated peak lists, instead of just comparing the intensities of correlated peaks. By doing so, the R-factor calculation is much less sensitive to 2theta errors and wrong peak assignments. In earlier versions of Endeavour, this problem frequently lead to wrong R-factor values and could prevent a whole crystal structure from being solved.
- Automatic space group determination from resulting structure
- Optional or automatic check/correction of 2theta errors.
- Automatic checking of peak correlations (optional, active by default).
- Several "advanced settings", e.g. flexible molecules, jump widths, peak triangles, Simulated Annealing parameters etc. - available from the structure solution wizard.
- Crystal structures containing molecules/rigid bodies can now be solved directly in a space group other than P1, even if their atoms must be placed on special positions.
- Viewing of the intermediate steps of the structure solution process: progress (% finished), R-Value and overall cost function, list of correlated calculated and observed peaks, structure picture, and diffraction diagram in user-defined arrangement side-by-side.
- Auto Build function to visualize the crystal structure of each intermediate step, e.g. the unit cell, with or without bonds, with or without polyhedras, molecules, etc.
- Report View displaying the results of Pareto optimization as formatted text, that can be copied to clipboard, saved, or printed.
- Easy editing, calculation, and fitting of potential parameters (simple repulsion, Lennard-Jones).
- Minimum interatomic distances for all element pair combinations (derived from Pearson's Crystal Data) are now implemented (no need for manual adjustment of parameters for the simple repulsion potential anymore)
- Support for molecular as well as for atomic crystal structures. Molecules can be fixed at certain positions and may rotate along a reference atom.
- Symmetry Finder with automatic or interactive transformation to higher space group.
- "Structure Solution" by either energy minimization or diffraction data alone is possible. Manual selection of rotatable bonds within the molecule(s) for variation during structure solution calculation.
- Import of 3-dimensional molecular structures from various file formats including Diamond (*.dsf), Cambridge CSD-FDAT (*.dat, *.fdat, *.csd), MDL Molfile/SDFile (e.g. from ACD ChemSketch) (*.mol, *.mdl, *.sd), Cerius2 CSSR (*.cssr, *.dat), Sybyl MOL/MOL2 (*.mol, *.mol2) and CIF (*.cif) files.
- Molecules can also be sketched and transformed into 3D using ACD ChemSketch Freeware which can be installed from the Endeavour 1.x CD-ROM.
Structure Visualization:
- Settings for the structure visualization "Autobuild" function (e.g. molecules, polyhedra) are now adjusted automatically, taking into account the "chemistry" of the compound under investigation
- Manual input or change of structural parameters and bibliographic data.
- Imports structure data from crystal structure databases (Inorganic Crystal Structure Database, Cambridge Structural Database, Protein Data Bank), from Pauling File (Inorganic Material Database), from Crystallographic Information File (CIF), from SHELX format, as well as from several molecular structure formats.
- Creating contents of unit cell, super-cell, or any arbitrary range of the crystal lattice.
- Discussion of connectivity assisted by histograms showing the distribution of distances between selected atom types, together with automatic calculation of distance ranges.
- Completion of coordination spheres around selected atoms.
- Generation of molecules or completion of molecular fragments that have been clipped at the cell edges (packing diagrams).
- Ball-and-stick, wire, and space filling model. Central or parallel projection, depth cueing, stereo display.
- Photo-realistic rendered models with user-defined light source and material properties (OpenGL).
- Rotating, shifting, and zooming: mouse-controlled, step-by-step by keyboard, or numerically. Views along specified axes or towards hkl-planes.
- Coordination polyhedra around selected atoms or manually constructed, with hatched, opaque, or transparent faces.
- Display of thermal ellipsoids to visualize anisotropic displacement parameters.
- Labelling of atoms and bonds. Variation of colors, styles and radii of atoms and bonds, either by type or individually assigned.
General:
- 32 Bit MS Windows application with tabbed Multiple Document Interface (MDI), context-sensitive menus, and toolbars. Allows "simultaneous" handling of multiple structures.
- User-defined arrangement of structure picture and diffraction diagram as well as several textual data side-by-side.
- Multiple-step Undo and Redo function.
- Calculation or interactive measuring of distances, angles, and torsion angles, including standard uncertainties.
- Export to crystal and molecular structure formats, peak and |F(hkl)| formats, Windows metafile, several bitmap formats, as well as to Virtual Reality Modelling Language (VRML).
- Online update (automatic or manual).
系統需求
System requirements
- Personal computer with MS Windows® XP, Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8/8.1 or Windows 10 operating system (does not run on Windows RT or Windows 10 S or Windows 10 in "S mode")
- Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.01 or higher
- 64 MB of RAM
- 100 MB of free disk space
- Graphics resolution of 1024 x 768 pixels with 32,768 colors ("High Color")
Match! is an easy-to-use software for phase identification from powder diffraction data. It compares the diffraction pattern of your sample to a database containing reference patterns in order to identify the phases which are present. Additional knowledge about the sample like known phases, elements or density can be applied easily.
In addition to this qualitative analysis, a quantitative analysis (using Rietveld refinement) can be performed as well. You can easily setup and run Rietveld refinements from within Match!, with the actual calculations being performed automatically, using the well-known program FullProf (by J. Rodriguez-Carvajal) in the background. Match! provides a gentle introduction into Rietveld refinement, from fully automatic operation to the "Expert" mode. The software runs natively on Windows, macOS and Linux.
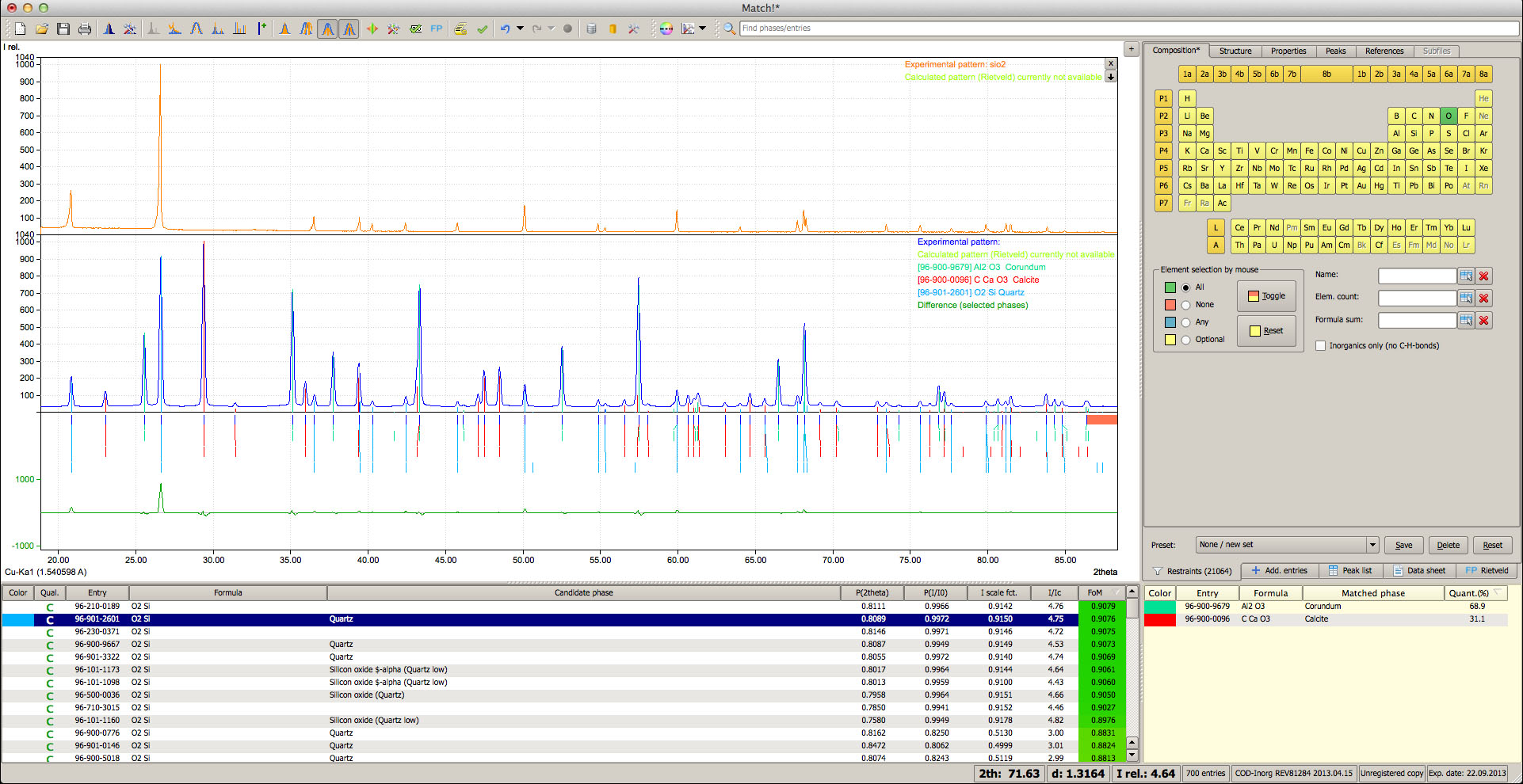
特色
- Rietveld refinement (using FullProf)
- Match! provides a gentle introduction into Rietveld refinement, from fully automatic operation to the "Expert" mode. With just two mouse clicks, you can easily transfer your data (diffraction pattern and crystal structures) to the FullProf software and run a Rietveld refinement.
- Indexing (unit cell determination; (using Treor or Dicvol)
- Indexing is a mandatory step in crystal structure solution from powder diffraction data, e.g. using our software package “Endeavour”. Knowing the unit cell can also be very useful in phase identification, considering that cell parameters can be used as restraints. Quite a lot of indexing programs are available today; Match! can use two of the most prominent: Treor90 and Dicvol06.
- Structure solution from powder (using Endeavour)
- Indexing is a mandatory step in crystal structure solution from powder diffraction data, e.g. using our software package “Endeavour”. Knowing the unit cell can also be very useful in phase identification, considering that cell parameters can be used as restraints. Quite a lot of indexing programs are available today; Match! can use two of the most prominent: Treor90 and Dicvol06.
- Runs on Mac, Linux and of course Windows
- No matter which one of these operating systems you prefer, Match! will run on it. Of course, you can use document files created with Match! on one platform on any other platform as well.
- Display and compare multiple diffraction patterns
- Additional experimental patterns can now be imported and displayed on top of each other, so that you can compare them to the main experimental pattern.
- Directly view specific phases/entries
- You already know that a certain phase is present in the sample, or you would like to check how some compound compares to the experimental diffraction pattern? That's pretty easy with the new version!
- Instant usage of additional information
- Additional information about the sample like elements that may be or must not be present, the density etc. can now be applied much easier than in the previous version.
- Saving of selection criteria
- Once you have entered a set of selection criteria (e.g. elements, density etc.) that best suits your requirements, you can save it using an appropriate name, and recall it later on with just two mouse clicks.
- Comfortable definition of background
- Simply insert, shift or delete control points in the automatically calculated background curve using the mouse, in order to precisely define the background with regard to the raw data.
- Improved zooming facilities
- Zoom now also implies zooming on the intensity (and not only on 2theta) axis. In addition, you can now simply use the mouse pointer and wheel to zoom into the area of interest. Of course, it is also possible to zoom to an exactly defined area (2theta/intensity).
- Batch Processing and Automatics
- You are a beginner or an expert user? As you like it: Simply adjust your skill level, in order to either give you full control at each single step, let Match! run the complete phase identification automatically, or anything in between.
- Crystallite size estimation
- Once you have achieved a good fit of the peak data to the experimental profile, you can let Match! calculate crystallite size values based on the peak's FWHM values, using the Scherrer formula.
- Manual Entries
- While match list entries (i.e. entries/phases that have been decided on as being present in the sample) normally correspond to entries in the current reference database, it is also possible to add so-called "manual entries" (or phases) directly from scratch, e.g. by importing crystal structure data or entering them manually. It is even possible to enter only partial crystal structure data sets (e.g. containing only unit cell parameters but no space group or atomic coordinates).
- Fast single and multiple phase identification from powder diffraction data
- Qualitative as well as quantitative analysis (DOC, internal standard)
- Runs on Windows, macOS and Linux
- Use free-of-charge reference patterns calculated from the COD (incl. I/Ic), any ICDD PDF database, any old ICSD/Retrieve version (released 1993-2002; valid licence required) and/or your own diffraction data (or patterns calculated from crystal structure data (e.g. CIF files)) in phase identification
- Perform Rietveld refinement calculations, e.g. for quantitative analysis, using the well-known FullProf in the background
- Flexible handling of reference databases (incl. user databases); you can easily switch between different reference databases without the necessity to perform a new database indexation
- Create reference databases for X-ray and neutron diffraction e.g. from cif-files
- Comfortable user database manager for easy maintenance of user data (add/import/edit/delete/sort entries)
- Powerful CIF- and ICSD/Retrieve import, incl. calculation of powder pattern, I/Ic and density
- Atomic coordinates available e.g. in the ICSD, the ICDD PDF-4+ or free-of-charge reference data are displayed in the data sheets and included in the CIF- or Textfile-exports (e.g. for Rietveld analysis)
- Displaying of Miller indices (hkl) in diffraction patterns and entry data sheets
- Fully integrated handling of your own diffraction data with PDF data (search-match, retrieval, data viewing)
- Automatic residual searching with respect to identified phases
- Automatic raw data processing: α2-stripping, background subtraction, peak search, profile fitting, error correction
- α2-stripping is not required for peak searching, search-match, phase identification etc.
- Automatic optimization of peak searching sensitivity
- Fitting of all (or selected) peak parameters to exp. profile data
- Comfortable manual editing of peaks (add/shift/delete/fit) using mouse or keyboard
- Semi-quantitative analysis (Reference Intensity Ratio method)
- Straight-forward usage of additional knowledge (composition, PDF subfiles, crystallographic data, color, density etc.)
- Integrated database retrieval system and viewer for PDF, COD and user databases
- Multiple step undo/redo
- User-configurable automatic operation
- Automatic d-value shifting during search-match process (optionally)
- Intensity contribution to figure-of-merit can be reduced for preferred-orientation cases
- Comfortable graphical and tabular comparison of peak data and candidate patterns
- User-configurable reports (HTML, PDF or text file)
- Viewing of crystal structures in Diamond (Windows version of Match! only)
- Online update (automatic or manual)
- Supported diffraction data file formats (automatic detection):
- ASCII profile (start, step, intensities or 2 columns)
- Bruker/Siemens raw data (old and new) (*.raw)
- Bruker/Siemens DIFFRAC AT peak data (*.dif)
- DBWS (*.rfl, *.dat)
- DRON-3 (still experimental)
- ENDEAVOUR peak list (2 columns: 2theta/d intensity; *.dif)
- G670 raw data (*.gdf)
- GNR raw data (formerly Ital Structures) (*.esg)
- Inel raw data (*.dat)
- Jade/MDI/SCINTAG raw data (*.mdi)
- JEOL ASCII Export raw data (*.txt)
- PANalytical XRDML Scan raw data (*.xrdml)
- PANalytical/Philips peak data (*.udi)
- PANalytical/Philips raw data (*.rd, *.udf)
- Rigaku raw data (both binary as well as text files containing '*'-keywords)
- SCINTAG raw data (*.raw, *.rd)
- Seifert
- Shimadzu raw data (*.raw)
- Siemens (*.uxd)
- Sietronics XRD scan data (*.cpi)
- Stoe raw data (*.raw)
- Stoe peak data (*.pks)
- TXRD export text files (*.txt)
- XPowder raw data (*.plv)
- XRDML raw data (*.xrdml)
系統需求
System requirements (minimum)
Windows
- Personal Computer with Microsoft Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7, 8/8.1, 10 or 11 operating system (32- or 64-bit)
- 2 GB of RAM
- Hard disk with minimum 2.5 GB of free disk space
- Graphics resolution of at least 1024 x 768 pixels (1280 x 800 pixels or more recommended)
- FullProf release January 2018 (or later) required for Rietveld refinement
macOS
- Mac with Intel or Apple M1 processor and macOS 10.12 "Sierra" operating system (or later)
- 2 GB of RAM
- Hard disk with minimum 2.5 GB of free disk space
- Graphics resolution of at least 1024 x 768 pixels (1280 x 800 pixels or more recommended)
- FullProf release March 2018 (or later) required for Rietveld refinement
Linux
- Personal Computer with Linux (Intel 64-bit) and glibc 2.27 (or higher)
- 2 GB of RAM
- Hard disk with minimum 2.5 GB of free disk space
- Graphics resolution of at least 1024 x 768 pixels (1280 x 800 pixels or more recommended)
- FullProf release February 2018 (or later) required for Rietveld refinement
Pearson's Crystal Data
Crystal Structure Database for Inorganic Compounds
Pearson's Crystal Data is a crystallographic database published by ASM International (Materials Park, Ohio, USA), edited by Pierre Villars and Karin Cenzual. It has its roots in the well-known PAULING FILE project and contains crystal structures of a large variety of inorganic materials and compounds. The "PCD" (as it is typically abbreviated) is a collaboration between ASM International and Material Phases Data System, Vitznau, Switzerland (MPDS), aiming to create and maintain the world's largest critically evaluated "Non-organic database".
The current release 2018/19 contains about 319,000 structural data sets (including atom coordinates and displacement parameters, when determined) for about 180,200 different chemical formulas, roughly 19,400 experimental powder diffraction patterns and about 297,000 calculated patterns (interplanar spacings, intensities, Miller indices). In addition over 46,000 figure descriptions for such as cell parameters as a function of temperature, pressure or concentration are given. To reach this result, scientific editors have critically analyzed and processed over 103,200 original publications.
The database comes with an innovative retrieval software for Windows PCs developed by Crystal Impact. It offers a large variety of new elaborate new features which make retrieval of the desired information extremely easy and comfortable.
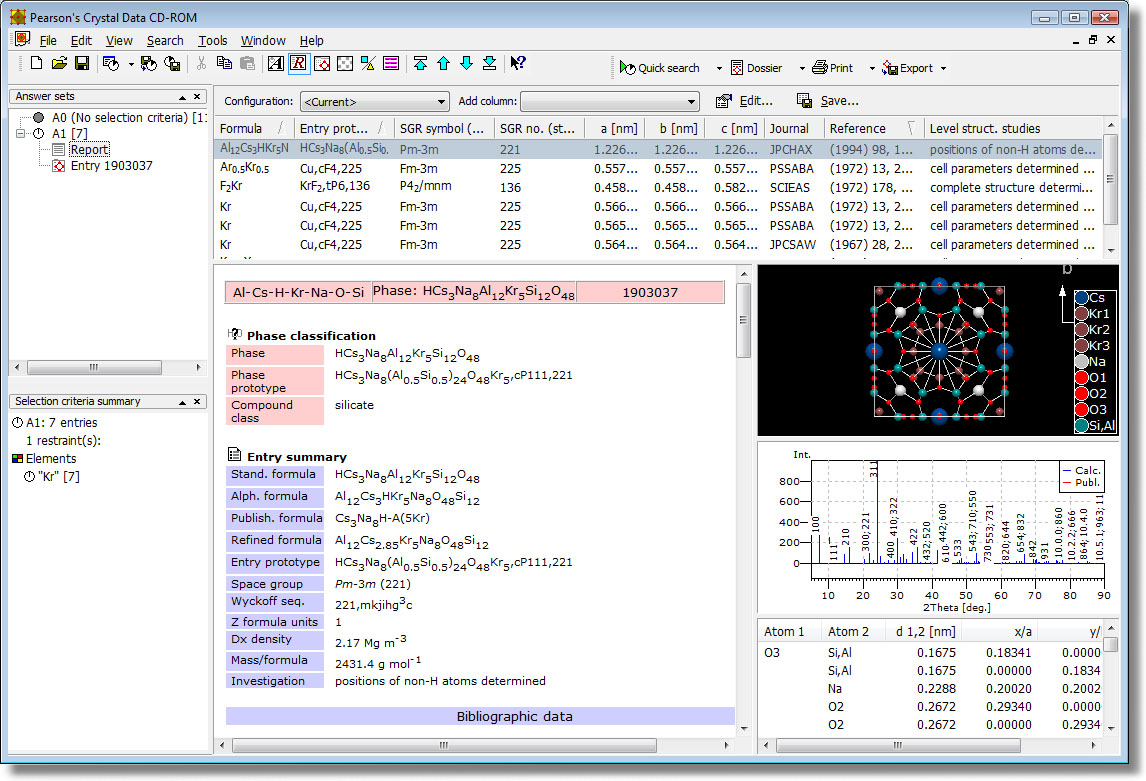
Database Features
- Comprehensive world literature coverage from over 108,000 original publications.
- Phase information available due to distinct phases concept, with the prototype entry being selected by editors for each individual entry:
- phase defined by crystal structure (prototype) and chemical system,
- every phase has been given a unique formula ("phase formula").
- Fully standardized and comparable crystal structure data.
- Both published as well as standardized crystallographic data are present, with assigned atomic coordinates if a prototype could be assigned but atom coordinates were not determined.
- Inclusion of Pearson Symbol, Prototype, Wyckoff Sequence classifications.
- Inclusion of derived data: interatomic distance, coordination number, atomic environment.
- Atomic environment type (coordination polyhedron) specified for every atom of the parameter list of a prototype structure.
- General and editor's remarks, information about preparation and experimental details.
- Data were checked using an elaborate software package containing more than 60 modules.
- 10,000 corrections of chemical formulas, cell parameters, symmetry or atom coordinates, applied and reported in errata.
- An entry contains more than twice as many database fields per entry than ICSD or Crystmet entries.
- Current release (2019/20) contains about 335,000 entries for about 188,000 different chemical formulas.
- Excellent coverage of alloys and intermetallics as a consequence of its origin (Pearson's Handbook of Crystallographic Data for Intermetallic Phases).
- Includes roughly 20,100 experimental powder patterns and about 297,000 calculated diagrams (interplanar spacings, intensities, Miller indices).
- Over 50,000 figure descriptions for cell parameters as a function of temperature, pressure, or concentration.
- Every entry contains links to external data sources:
- ASM International Alloys Phase Diagrams Centre Online
- SpringerMaterials consisting of
- Landolt-Börnstein
- Pauling File Multinaries Edition 2009 (Springer)
- Original publication (through crossref.org).
Software Features
- Perpetual restrainting: always see what you get (intermediate as well as final matching entry counts) while you edit the selection criteria
- List selection boxes ("quest dialogs"): View and select all available values for a database field (selection criterion) using the mouse
- Two alternative dialogs for the input of the selection criteria: quick and exhaustive
- Visualization (3D pictures) of crystal structures
- Elaborate data views at different "levels":
- Entry report (answer set level)
- System matrix (chemical system level)
- Phases list (phase level)
- Entry data (entry level):
- Data sheet:
- Link to Phase Diagrams Online
- Link to original publication (if available online)
- ICDD PDF number (if available)
- Dynamic plots (cell parameters against temperature or pressure)
- Figure plots prepared by the editors
- 3D structure picture:
- visualization of atomic environments/coordination polyhedra
- distance statistics
- manual measurement of selected distances and angles
- four different models available (ball-and-stick, wires, sticks, space-filling)
- color differentiation according to element or Wyckoff position
- Powder diffraction pattern:
- calculated pattern for user-defined wave length
- published pattern (if available)
- zoom in/out
- tracking (simultaneous zoom and pattern shifting using the mouse)
- Table of distances and angles:
- 3D picture of selected atomic environment
- distance statistics histograms
- Radii/volumes diagram for comparison of similar crystal structures
- Elaborate data selection beyond the normal selection criteria dialogs:
- Searching for entries with same prototype
- Logical combination of arbitrary answer sets
- Creation of answer set from:
- selected entries
- selected phases
- selected chemical systems
- Cut/copy/paste of selected entries
- Compilation of phase data sheet from user-selected entries
- Conversion tool for standardization/Niggli-reduction of unit cell parameters
- Search for:
- interatomic distances
- phase information (e.g. phase formula, phase prototype, mineral name)
- chemical composition
- atomic environment (coordination number, atom coordinations)
- crystallographic data and classifications
- structure determination details
- processing information (e.g. PDF-number)
- bibliographic data
- Printing of all kinds of information and views:
- Dossier (containing all/selected database field values and graphics for one entry each)
- Data sheet
- Tables (e.g. powder diffraction pattern, distances and angles)
- Graphics (e.g. structure picture)
- Export of:
- Entry data (e.g. as CIF-file)
- Tables (e.g. powder diffraction pattern, distances and angles)
- Graphics (e.g. structure picture)
- Diamond document (single-click transfer of structure data and picture to Diamond software for further investigation or structure picture modification)
- Retrieval through dynamically updated restraints drop down listings and/or counts vs. numerical values plots (no keyboarding needed)
- Creation of individually tailored Phase Data Sheets and Data Dossiers
- Complete flexibility to edit an entry report by adding a column with another database field, or moving or deleting columns, as well as sorting
- Comparison of nearest neighbor histogram of any specific atom with its statistical plot containing all distances in the database
- Dynamic changes of the selected atomic environments by clicking on its nearest neighbor histogram
- Searching for pre-defined atomic environments (coordination polyhedra) including selection criteria to the central atom and to the coordination atoms, as well as its interatomic distances
- A session together with its answer sets, selection criteria, and visited views can be stored and used as a starting point for next session.
系統需求
System requirements
- Microsoft Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7, 8/8.1 or 10
- (Note: Does not run on Windows RT and Windows 10 "S" or Windows 10 in "S mode")
- Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.01 (or higher)
- 1 GB of RAM (2 GB or more recommended)
- 4 GB of free disk space
- Minimum graphics resolution of 1024x768 pixels with at least 32,768 colors


.jpg)