Nemasis 是一個網路漏洞管理套件,可檢測網路中的漏洞並提供準確的解決方案來修復漏洞。
它説明您管理您的組織的整體治理、風險和遵守法規。
Nemasis 旨在保護您和您的組織免受網路安全威脅,並確保全天候受到保護。
下面我們提到了Nemasis 的主要特徵:
• 掃描通過網路連接的端點,以尋找漏洞。
• 報告發現的漏洞並提供準確的解決方案來修復它們。
• 監視組織中端點的安全狀態。
• 創建和管理端點的掃描任務。
• 根據您的喜好發送自訂的掃描任務警報和報告。
• 持續監控網路的被動漏洞掃描器。
• 通知在通過網絡連接的系統上運行的開放埠、惡意應用程式或服務。
隨著技術的發展,威脅也在不斷演變。但是,有了Nemasis,我們確信您的組織運營將平穩運行。
Nemasis 遵循最佳的行業安全合規性和監管框架,可説明您加強 IT 安全、提高工作效率並按時實現業務目標。
MicroWorld Technologies的Nemasis是一個漏洞管理套件,可幫助實施全面的GRC(治理,風險管理和合規性)戰略,以管理組織的總體治理,風險和合規性。Nemasis與GRC策略的集成有助於管理安全性和合規性,從而降低總體業務風險。Nemasis GRC具有多種優勢,例如消除了冗餘成本,深入執行漏洞掃描,優化了投資,確保了商業信譽,資產發現等。
Nemasis用於掃描網絡漏洞,例如開放端口,每個系統上運行的應用程序以及活動服務。Nemasis根據NIST,OVA,世界機構等生成許多類型的報告。幾乎所有平台,系統,應用程序,數據庫,設備和瀏覽器都支持Nemasis。
Nemasis - VA (Vulnerability Management for Enterprises)
Scalability and Flexible Deployment
The systems and network infrastructure of each organization are distinct. Nemasis provides you scalable and flexible deployment option based on the requirement (volume of scanned IP's). To increase the speed and accuracy of your assessments, the ability to optimize your VMS according to the specific needs of your organization is very important. As your organization develops, your VM solution should be able to grow quickly and easily just by adding scan engines to your current deployment at minimal or no additional cost. Nemasis helps to scale your VM simply by adding Scan engines to your current deployment, and additionally, it helps you to configure the concurrent Scan Plugins and Number of hosts with respect to a single scan.
Prioritization
Nemasis dashboard and reports offer a granular representation of vulnerabilities with respect to the CVSS and also provides the total risk scenario for any scan. It also provides statistical data based on days/month/year in a real-time dashboard. False positive function is also provided as a temporal metric for Vulnerabilities which are accepted risk scenarios by the organization and can be defined in the range of Low/Medium/High/Log/False Positive. Nemasis also provides host tagging, which is available based on Owner/Groups wherein, the criticality levels can be defined that will publish the priorities based on the final score in a report. Nemasis also provide our own internal threat intelligence gathering, which can be prioritized based on their criticality level.
Internal and External Scanning
The only reason, Nemasis suggest using both internal and external vulnerability scan is to understand the scope of vulnerabilities inside and outside your organization, as threats can emanate from anywhere. The internal scan assesses your network security from inside your firewall, which can be both with/without credentials. The external scan is performed remotely from outside, which is normally non-credential/unauthenticated scans.
Credential Management for Authenticated Scans
An authenticated Scan scans the target network from both, external via the network and from the internal via a valid user login. Nemasis provides an SNMP authentication scan which mostly scans network devices, SMB authentication scans which checks the patch level and locally installed software for Windows, SSH authentication scans which checks for patch-levels on UNIX- and Linux-based systems, and ESXi authentication scans which tests the VMware ESXi servers locally.
Reporting
The reports are automatically sent as an email attachment once the scan is completed. Reports are available in different format such as HTML, PDF, TXT, RTF, and XML. These reports are interactive by nature when viewed on the Nemasis console. Reports generated in XML formats make it possible to integrate reports with third-party software like SIEM, CRM Analyzers, and more. Reports generated in CSV format can be exported as XLS, where further filtering such as Severity, Software, protocol, and many more can be done. Remediation report validation can be done by re-scanning the whole network or system. Nemasis helps you to customize your reports according to the specific need of the organization, for example, based on tagged asset groups, severity, and many more.
Compliance and Configuration Assessment
Nemasis allows fast-track the compliance assessments of network, web application, and infrastructure according to industries standard and best practices such as Center of Internet Security (CIS), Payment Card Industry (PCI), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), OWASP 2010, and many more. Each compliance report template has its own uniqueness in assessment, for example, PCI is specifically used for protecting and securing the cardholder details. Use this report template to generate a compliance report for PCI assets and the report gives you all the security precautions to protect your assets. It also performs and generates a unified report of configuration and compliance assessment. Nemasis not only has a compliance report template but also allows customizing the reports according to specific business needs which makes it stand out.
Remediation
Combine patch management capabilities of your patch management system with the scan data from Nemasis, and apply patches to vulnerable assets without delay. Use Nemasis to Verify High Severity Vulnerabilities and patch or fix them without delay. Using Remediation Projects you can build dynamic projects that track vulnerabilities related to Microsoft patches as they are identified in your environment. Nemasis allows you to report the vulnerability based on various options such as CVSS, Scan plugins, Port/Protocol/Services, and Patches like OS patches, application patches, and more. For example, Using patch option Nemasis can leverage credentials for the patch management systems to perform patch auditing on systems for which credentials may not be available to the Nemasis scanner. Scan plugins are tested against the host and Nemasis display the data reports gathered from Scan plugins.
Nemasis not only helps in identifying the risk but also prioritizes the risk and provide a remediation plan. This remediation plan is then automatically sent to the owner so that the risk is prevented as and when identified. It also helps to identify weak points in the remediation workflow to identify the problems and tracks your progress.
Management and Administration:
Nemasis Dashboards are interactive by nature and provide specialized views of your network in a customizable and drag-and-drop interface along with the real-time data. You can add, delete, and move the dashboard according to your preferences, and choose the order in which they should appear in the module. Nemasis use components such as Scan Display, Asset Display, SecInfo Display and many more to generate multiple dashboards.
Nemasis allows you to configure and manage different users with different sets of roles and permissions. The administrator is being created by default and is allowed to login and manage the additional users. Nemasis user management supports to create role-based users who have permission to view and modify the web interface, to assign the read and write access to the user separately, and to create groups. You can configure users who can access and login into the management console using LDAP and TNS integration. This is because if LDAP service at some becomes unavailable you can still login into the console using TNS authentication. You can perform functions based on roles, groups, and asset using LDAP and TNS authentication according to the organization needs.
Data Filtering Options
Asset data can be filtered by state (active/inactive), asset tags, service names, open ports, and service protocols. When dealing with a large number of network assets, it is necessary to filter out the assets on specific conditions or subsets. This helps you to focus your remediation efforts and to handle the assets running on a complex or distributed network. For example, you could build filters for a given IP address range, or a particular site, and then combine these filters to return a list of all the assets that meet the specified criteria. Nemasis provide a large number of search filters based on host, service and software names, CVE ID, IP address, PCI compliance status, and others.
Logging and Monitoring: (SIEM integration will be releasing soon)
Nemasis detects vulnerability in alliance with other log data sources such as SPLUNK, Office CRMs, which allow organizations to analyze, search, monitor, and visualize big data coming from websites, networks, sensors, applications, servers, and mobile assets. Splunk integration helps Nemasis to easily detect attacks, view security incidents, conduct extensive investigations, enables monitoring opportunities with deception technology. You can even get the detailed log of vulnerability, compliances, configurations, and many more through Nemasis dashboard, single log, and separate log. These logs can be exported in various formats like PDF, XML, text, and more. Also, these logs can be back up automatically in case of future use.
Dashboard Data Sources
Nemasis combine the information from the Scan plugins, CVE (Common Vulnerability and Exposures), and the CERT and displays real-time data easily in the web interface in dashboards. It displays the data on the dashboard based on the data gathered from the Scan plugins. Nemasis has a long list of vulnerabilities which is linked to relevant groups like Mitre and other CVE Numbering Authorities and uses them for further visibility.
Network Scan
Nemasis supports various types of network scanner such as TCP, WMI, UDP, SSH, SNMP, HTTP, SMB, and LDAP. Each of the scanners performs different sets of scanning. For example, TCP scanner scans all the ports that are vulnerable for attacks using Stealth scan (SYN) method while HTTP scanner checks for HTTP servers, web server options, and server configuration.
Distributed Scanner Support
Nemasis provides Master-Slave support for the purpose of superior distributed and load-balanced scanning and these scanners can be distributed throughout an entire Enterprise. The Nemasis scanner features high-speed discovery, configuration auditing, asset profiling, and vulnerability analysis of your security framework. Distributed scanning helps to scan the large/distributed network in very less time by putting less stress on the network infrastructure.
Container Assessment: (This feature will be releasing soon)
Nemasis VMS will identify and prevent vulnerabilities throughout the entire application lifecycle while prioritizing risk. It will help the developers to integrate VM into their CI process, while security teams want to continuously monitor, identify, and prevent risks to all the containers, images, and hosts in their infrastructure.
Alerting Actions
Nemasis identifies thousands of threats from the endpoints of the network by constant monitoring. However, huge numbers of activities are not serious threats but will cause alarm or set off alerts, which help security teams to proactively be alerted about potential threats so problems can be tackled before turning into breaches. Alerts can be customized according to the need of the user depending upon the risks such as open ports, SSL certificates, and unwanted services and software. You can define different groups for different sets of alerts, and you can design individual alerts over different timeframes.
Agent-based Scanning: (Agent-based solution will be releasing soon)
Nemasis, for now, provides the agentless solution. In the near future, Nemasis agent-based solution will be well suited for performing power management tasks. Agents need to be easy to install and lightweight so as not to take up much network bandwidth. This is ideal for distributed networks with remote locations that have limited bandwidth, based on pull technology. It will enable in-depth scanning of a system without providing system credentials, and it performs patch management and asset management tasks on disconnected machines.
Passive Vulnerability Scanner
Nemasis PVS plugin is an exclusive network discovery and vulnerability testing software that delivers real-time network profiling and monitoring for constant and continuous assessment of an organization's security demeanor in a non-intrusive manner. It continuously monitors the assets, such as servers, desktops, laptops, network devices, web apps, virtual machines, mobile, tablets, cloud-based assets, and more, that use IP protocol to determine topography, services, and vulnerabilities. It also tracks the network changes within your organization's infrastructure. Nemasis provides OS fingerprinting, Service fingerprinting, database password management, and more configuration (Limited Configuration) for Windows platform is currently available. Nemasis inbuilt Passive Vulnerability Scanner has a capability that will allow you to provide the discovery and the network topology.
Updates, Support, and License
Nemasis provides the application update both automatically and manually. There are regular updates on the new vulnerability that are being added to your database. The License provided by Nemasis is based on the number IPs within the organization and it covers only hotfixes, minor or major updates but also the new version of the solution. We offer 24x7 free online technical support to our customers through e-mail and live chat. We also provide free telephonic support to our customers during our business hours. The Nemasis technical support team is available round the clock to assist you with your queries. If you have any queries, suggestions, and comments regarding Nemasis, please write to us at [email protected].
Audit Policy Management
Performing regular audits of configuration settings on your assets may be necessary for your organization. You may need to verify that your assets meet a specific set of configuration standards such as USGCB 2.0 policies, USGCB 1.0 policies, FDCC policies, CIS benchmarks.
Discovery
Before you start scanning the network, you should know what assets you have so that you can manage the risk easily. Nemasis helps you to provide a range of IPs to scan them using Host Discovery Scan option and also asset can be tagged to owner/groups.
Integration: (Hybrid, that is, agent-based will be releasing soon)
The virtual and cloud asset's risk to safeguard the environment is identified and assessed dynamically by our Nemasis on-premise solution. While Nemasis hybrid solution has the capabilities to perform the host scanning with the help of access levels granted by the cloud services provider. Nemasis integrate with Syslog, Splunk, and other orchestration tools which allow organizations to analyze, search, monitor, and visualize big data coming from websites, networks, sensors, applications, servers, and mobile assets. Nemasis will also integrate with the enterprise ticketing system and RESTful APIs, which can be custom configured according to the organization's specific need.
Nemasis – DAST (Web Application Security Framework)
Nemasis Dast掃描外部的網站和Web應用程式,並在運行狀態下識別其中的漏洞和安全問題。它運行在操作程式碼上,以 interfaces, requests, responses, scripting, data injections, sessions, authentications 等方面的問題。以下是Nemasis – DAST的主要優點:
- Scanners are built with a crawl and attack architecture.
- Scans for hidden and other exploitable vulnerabilities (XSS, SQL injection, and other listed in OWASP Top 10).
- Comprehensive application coverage and sophisticated attack methodologies.
- Compatible with web applications built on PHP, ASP, Java, or any other language.
- Internal and external web applications scanning.
Web Applications
In the era of globalization, web-applications are turning to become a part of the IT assets of an organization. The open-source or third-party developed web-based applications are enabling organizations to ensure ease in conducting their business operations. Besides, various organizations are migrating from legacy systems to web-based applications, which provide them with centralized data warehousing capabilities. The digital threats have developed from attacking FTP, Telnet/SSH, and mail servers as a large number of services are exposed to the Internet have increased significantly, however, in recent years, web applications play a critical role in half of the breaches that happen around the world. Web applications have become the simplistic route for the hacker as they prove to be least resistant to infiltration and gain access to the internal network/resources of an organization.
Network scanners and assessment tools are responsible for validating and verifying the presence of vulnerabilities within the network and the accessible assets. However, in the case of a web application, it is the business logic which needs to be tested, since any Network Vulnerability Scanner would scan the web-servers and not the content which is being pulled away. The most common victims of web application breaches are Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress, Drupal, etc., Database Administration tools like phpMyAdmin, and SaaS applications. Web applications are developed using different frameworks and methodologies, which are designed to ensure faster delivery of the content to ensure business continuity.
Web Application Scanner/Application Security Audit
Web application scanner enables organizations to scan applications for vulnerabilities which may have been left exposed during the development cycle and it is an essential part of Enterprise Security Testing. Web applications are one of the most vulnerable facets of enterprise security – more than 50% of all successful data leaks and breaches comprises of web apps. IT Administrators and Developers would probably identify vulnerabilities inside the hosted applications like Cross-Site-Scripting (XSS) or SQL Injection (SQLi) as well as backdoors and other threats that hackers may exploit to attack an organization.
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) is a black-box security testing technique in which an application is tested in its operating state and tries to hack it just like a hacker would. A DAST test not only looks for a wide range of vulnerabilities, including input/output validation issues that could leave an application vulnerable but also facilitates the organization to follow the industry-based compliances.
Security threats posed by web applications
There are various drawbacks when it comes to relying on web applications for business processes. Web applications pose a significant threat to the digital environment of any organization with a myriad of vulnerabilities and attack vectors. The most important thing all organizations will have to address and guard themselves against the presence of software vulnerabilities and threats to web applications. While there is no 100% assurance for safety, there are some steps one can undertake to avoid wreak havoc. The OWASP Top 10 is a report document of security concerns for web application security. It represents a wide-ranging consent about the most critical security risks to web applications; however, an application may be vulnerable to a variety of attacks which may never make it to the OWASP Top 10.
Insecure Direct Object References
Web applications may provide a feature to download a file, however, the hacker is able to download any file from inside the system is one of the examples of Insecure Direct Object Reference. There have been instances wherein hackers have accessed sensitive data files/password files through this vulnerability.
Broken Authentication
When authentication functions related to the web application are not executed correctly, it enables hackers to compromise passwords or session ID's, data access URIs are accessible without authentication, or to exploit other implementation flaws using other users credentials to gain access to restricted areas or may leave the data disclosed.
Injection Attacks
Web application may contain defects which enable a hacker to inject code into the application or modify the requests/parameters which have not been disinfected. When an application requires more data, the chances for injection attacks are more. Some names of the injection attacks are SQL injection (SQLi), cross-site scripting (XSS), stored XSS Remote File Inclusion (RFI) and Local File Inclusion (LFI) which are the result of incorrect coding practices and are difficult to detect amid the development stage.
Security misconfiguration
Hackers depend on system errors & debug data to increase the understanding of a system, those are introduced due to a misconfiguration of the server. However, executing an application with known vulnerabilities is also a part of the Insecure Server Configuration. These attacks depend on the hacker’s knowledge of vulnerabilities which have been made publicly accessible, patches have been made available by the developers, and the server administrators have failed to implement the patches.
Mirai botnet exploited the Security Misconfiguration of the IOT devices and had successfully affected poorly protected Internet devices (IoT) by using telnet to exploit default username and password. Also, it has been one of the most successful botnets in the history of IT Security.
Summary of Features – Nemasis DAST
Web-Applications are prone to numerous vulnerabilities which can be harder to detect by manual testing. Nemasis-DAST uses Passive Scanning and Attack /Active Scanning modes to identify and exploit these vulnerabilities.
Passive Mode Scanning
|
Attack/Active Mode Scanning
|
Features – Nemasis DAST
Spider/Crawling
Nemasis-DAST’s spider is a tool that is used to automatically discover new resources (URLs) on a specific site. It starts with a list of URLs to visit, called the seeds, which depends on how the Spider is started. It then visits these URLs, it identifies all the hyperlinks in the page and adds them to the list of URLs to visit and the process continues recursively as long as new resources are found. Amid the processing of an URL, it makes a request to fetch the resources and then parses the responses, and recognizing hyperlinks.
Passive Scanning/Non-Intrusive Scan
Nemasis-DAST passively scans all HTTP messages (requests and responses) sent to the web applications and is safe to use since it does not change the requests or responses. This is performed in a background thread to guarantee that it doesn’t back off the analysis of an application. Passive scanning can also be used for automatically adding tags and raising alerts for potential issues which are provided by default.
Active/Attack Scanning / Intrusive Scan
Active scanning endeavors to discover potential vulnerabilities by using known attacks against the selected targets. It is an attack on those targets which you should NOT use on web applications that you do not own. It can discover vulnerabilities like broken access control; will not be found by any active or automated vulnerability scanning.
Scan Policy Management
This feature of Nemasis-DAST enables you to manage the scan policies that define the rules that are run while performing a scan. You can add the number of scan policies as you like, and choose which policy should be executed while you perform the scan. Once the scan policy is added you can modify or remove them. Also, you can directly import or export the scan policy.
AJAX Scanning
It is a security scanner used to evaluate the security of AJAX-enabled applications. By detecting the specific AJAX frameworks in use, Nemasis-DAST is able to better formulate test requests and identify potential vulnerabilities.
Critical Vulnerabilities Targeted
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
This is a web-based attack executed on the vulnerable web applications, the victim here is the user and not the application, and the malicious content is delivered to the user through JavaScript. To avoid this kind of attack web application should filter the user input to discard characters such as < and >. Also, you have to make sure that your server does not display error messages containing input received from the user.
Broken Access-Control
This is mostly poorly configured or missing restraints on authenticated users which enable them to access unauthorized functionality or data, such as viewing sensitive documents, accessing other users’ accounts, and modifying data and access rights. Nemasis-DAST detects where access controls are missing and the solutions to overcome them.
Broken Authentication and Session Management
Various types of vulnerabilities related to credentials authentication, session IDs exposure, and sending them through unencrypted connections will allow hackers to either capture or bypass the authentication that is used by the web application. To avoid these kind of breaches:
- Credentials should be protected using hashing or encryption
- Session IDs should not be exposed in URLs and should timeout,
- Session IDs should be recreated once the login is successful
- Credentials and session IDs should not be sent over unencrypted connections.
While it should also look for the password length and complexity, password and username enumeration, protection against brute force login. Also, the organization should use multi-factor authentication such as FIDO alliance and more to prevent the risk of compromised accounts.
SQL Injection
The SQL Injection attack is done without changing anything on the database side. To execute this, the test uses an incomplete (or incorrect) SQL statement which will cause the SQL server to throw an error. A hacker can then modify the payload to perform an actual attack. Since SQL commands are injected in an application form into the database, it is possible to change or dump the database’s sensitive data (like credit card details or passwords) so that they will be visible to the hacker. It is used to delete or change data or allow hackers to sidestep a login form without needing to guess the password. The solution for this is using stored procedures or parameterized queries to prevent hackers from altering the queries or prevent injection flaws.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
CSRF is an attack that includes forcing a victim to send an HTTP request to a target destination without their insight or intent in order to perform an activity as the victim. The idea of the attack is that CSRF exploits the trust that a website has for a user. CSRF attacks are not necessarily cross-site, yet they can be. CSRF is possible due to various factors such as the victim has an active session, is authenticated via HTTP Auth, or on the same local network on the target site. The risk of data disclosure is drastically increased when the target site is vulnerable to XSS because XSS can be used as a platform for CSRF, allowing the attack to operate inside the limit of the same-origin policy.
Sensitive data exposure
The most common defect is simply not encrypting sensitive data. When crypto is used, weak key generation and management, and weak algorithm usage are normal, especially weak password hashing methods. Browser weaknesses are very common and easy to identify, but difficult to exploit on a large scale. Hackers have difficulty in identifying server-side defect due to limited access and they are also usually hard to exploit.
Insufficient attack protection
Most applications and APIs identify invalid input, yet essentially dismiss it, giving the hacker chance to attack again and again. Such attacks indicate a malicious or compromised user probing or exploiting vulnerabilities. Identifying and blocking both manual and automated attacks is one of the best ways to increase security. Hackers use various automated tool and skilled humans to identify vulnerabilities and possibly exploit them.
Security Misconfiguration
Security misconfiguration attacks exploit configuration defect found in web and application servers. Administrative or debugging functions may be accessible to anonymous users which may provide a means for a hacker to bypass authentication methods and gain access to sensitive information which may require special privileges. Misconfigured SSL certificates and encryption settings, the use of default certificates, and improper authentication implementation with external systems to gain unauthorized access or knowledge of the system.
Under-protected APIs
Nowadays, modern web applications and APIs are increasingly made of rich clients (browser, mobile, desktop, and more) that connect to backend APIs (XML, JSON, RPC, GWT, custom). APIs (microservices, services, endpoints) can be vulnerable to the full scope of threats. Unfortunately, dynamic and sometimes even static tools don’t work well on APIs, and they can be difficult to analyze manually, so these vulnerabilities are often unfamiliar.
Using components with known vulnerabilities
The popularity of this issue is far-reaching. Some known vulnerabilities lead to only minor impacts, some of the largest breaches to date have relied on exploiting known vulnerabilities in components. Depending on the assets you are protecting, perhaps the risk should be at the highest priority on the rundown.
Reports
Scanning report-based on the Threat Level (High, Medium, Low or Information-only) of all the affected URIs
The report will contain the list of affected URIs and the threat to which it is exposed to. It is listed on the basis of threat-level, that is, high, medium, and low. Vulnerabilities with high threat level are categorized as the most dangerous, which put the target scanned at maximum risk for hacking and data theft. While vulnerabilities with medium threat-level are caused by server misconfiguration and site-coding flaws, which facilitate server disruption and intrusion and vulnerabilities with low threat-level are derived from lack of encryption of data traffic or directory path disclosures.
Threat Severity Classification (WASC)
This report displays WASC threat classification issues found on your web applications or website. The Web Application Security Consortium (WASC) is an international group who produces open-source and widely agreed upon best-practice security standards for the Worldwide Web. If any vulnerability is identified, performing the attack requires using at least one of several application attack methods. These methods are generally referred to as the class of attack. The WASC web application threat severity classification has a list of attacks which includes Brute Force attack, XXS, DoS, Path Traversal, and many more.
Weakness Classification (CWE)
The Common Weakness Enumeration Specification (CWE) is a community-developed list of common software security weaknesses. It serves as a common language, a measuring stick for software security tools, and as a baseline for weakness identification, mitigation, and prevention efforts. The CWE has the list of common software weaknesses which serves as a process for describing code vulnerability assessment capabilities in terms of their coverage of the different CWEs.
Remediation for discovered vulnerabilities
This provides a list of vulnerabilities identified while performing a scan on the web applications. It also prioritizes the risk of the vulnerability detected and provides the remediation plan for them.
Minimum system requirements
ISO can be installed on following virtual environments
- VMware
- Microsoft Hyper-V
- Oracle Virtual Box
Appliance details/Minimum system requirements
- 2 CPUs
- 8 GB RAM
- 50 GB HDD
Supported Platforms/Browsers
Supported Platforms
Supported Devices/Systems /platforms/ applications
- Network devices
- Virtual Systems: VMware ESX, ESXi, etc.
- Operating systems: Windows, Mac, Linux, etc.
- Databases: Oracle, SQL Server, etc.
- Web applications: Web Servers, Web Services, OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities
- IPv4/IPv6/Hybrid Networks
- Cloud Systems
BROWSERS (with HTML 5 compatibility)
You can use Nemasis with popular browsers such as below:
- Google Chrome (RECOMMENDED)
- Mozilla Firefox
- Mozilla Firefox ESR
- Safari 7.1
- Safari for iOS
- Microsoft Edge
- Microsoft Internet Explorer 11
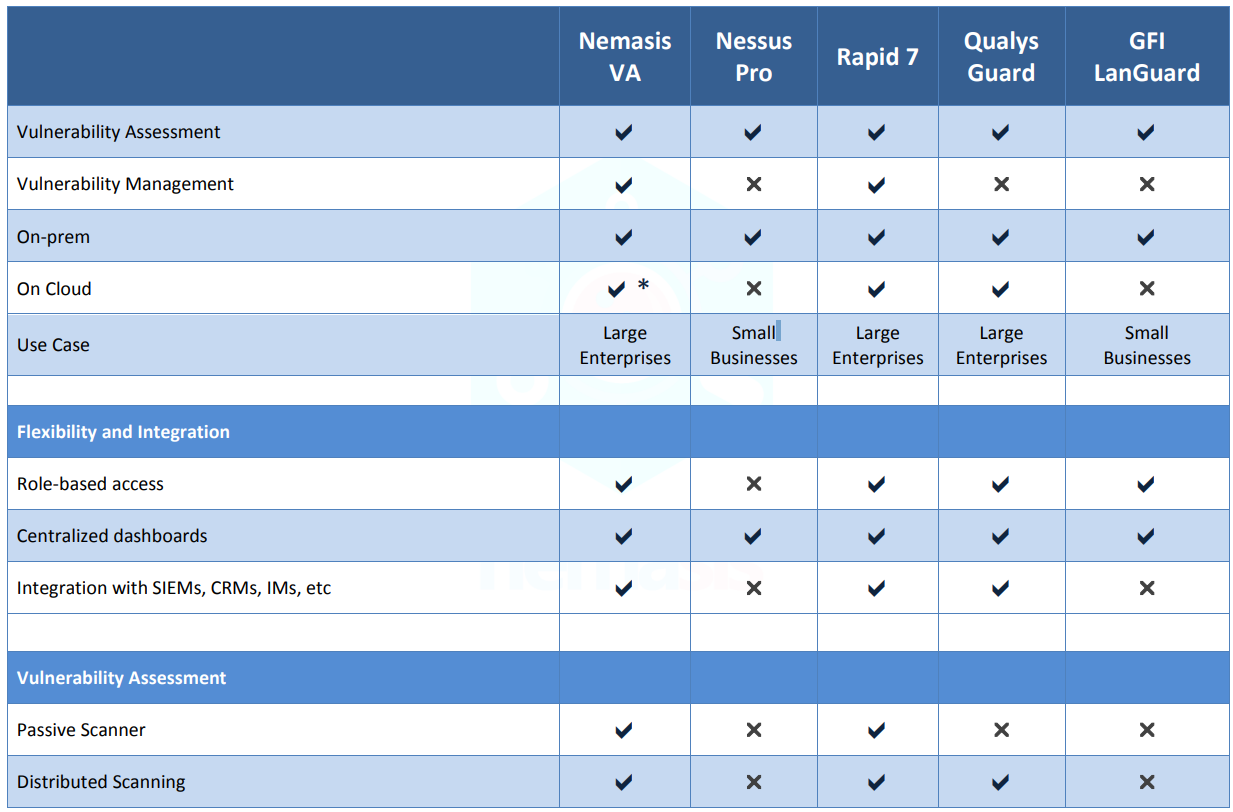
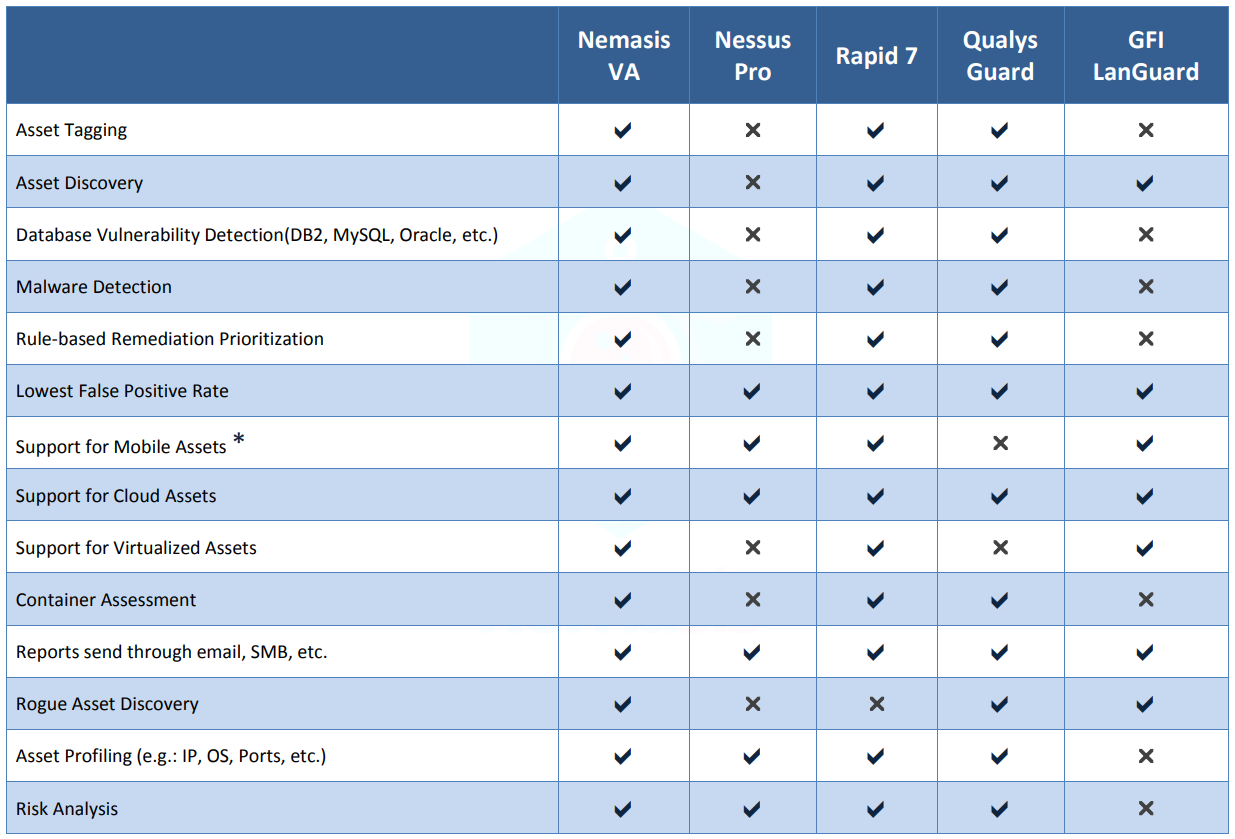
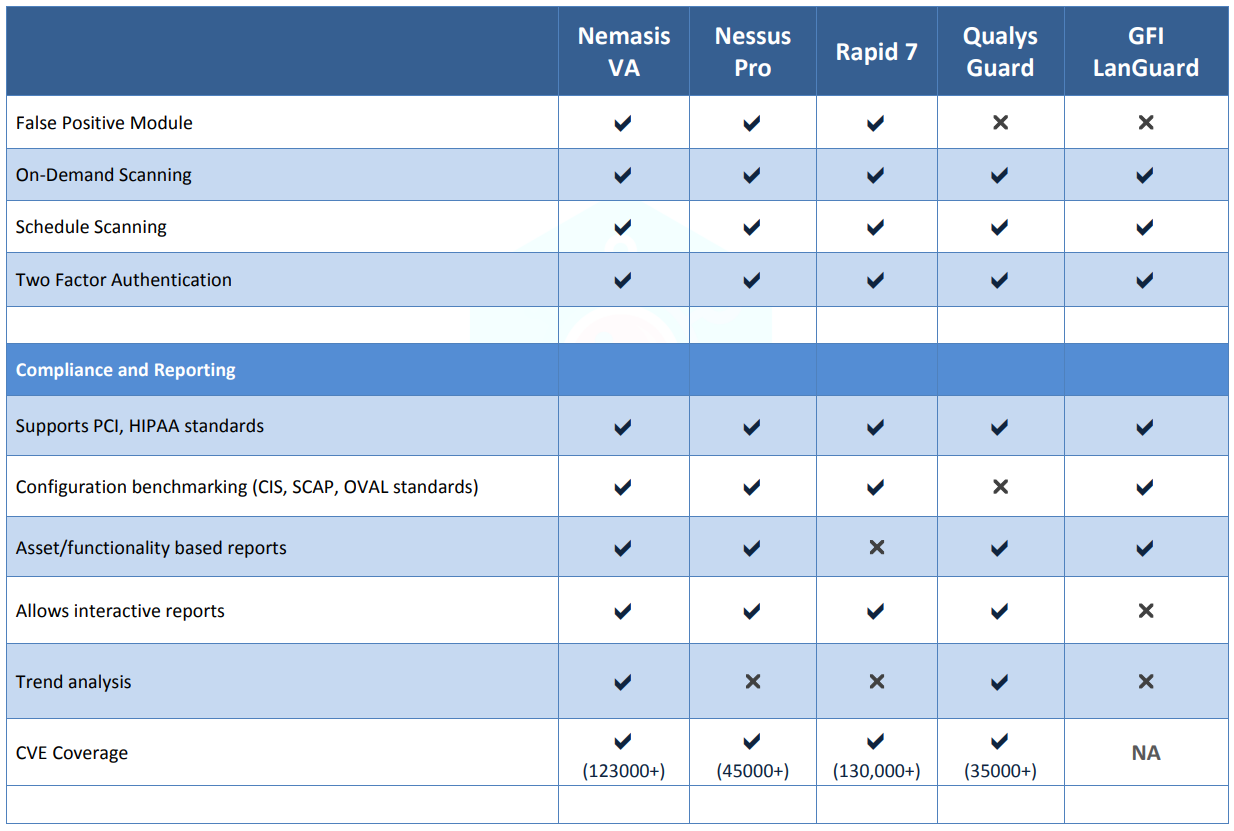
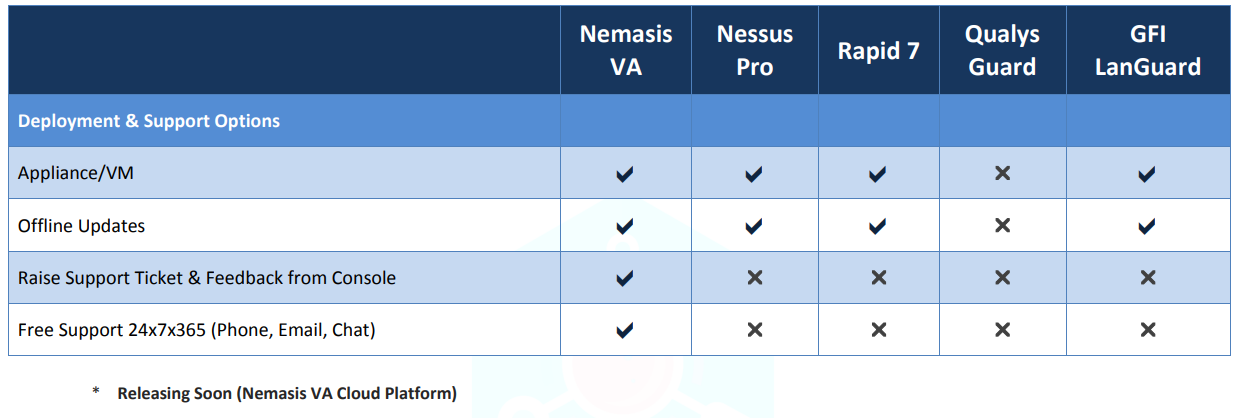
Nemasis VA vs Nemasis Pro vs Rapid7 vs Qualys vs GFI Languard
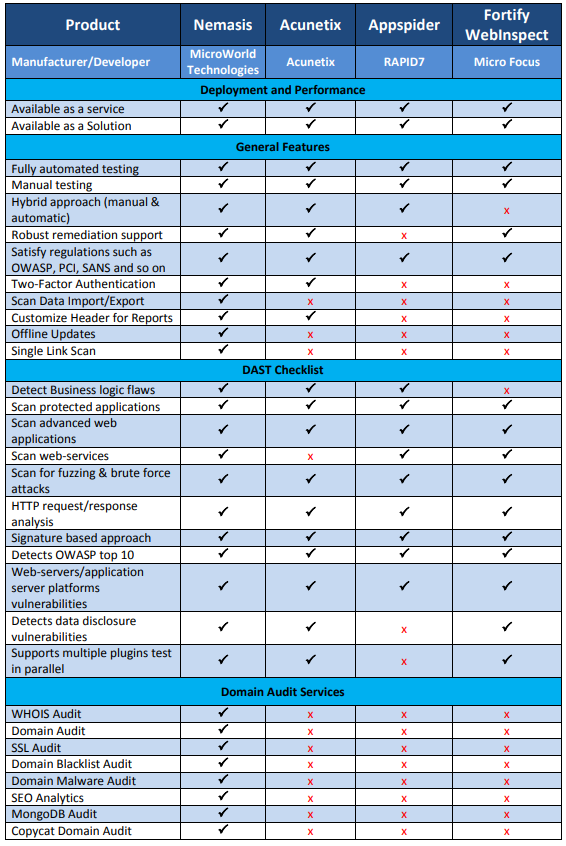
Nemasis DAST vs Accunetix vs Appspider vs Fortify Webinspect